Difficult Templates
Sequence context often plays a role in how well a template will sequence. The following are some common sequence content that poses an issue for the polymerase. Contact the Genmomics Core staff to discuss strategies to overcome difficult template issues.
GC-Rich Sequence
DNA with a high GC-content can be difficult to sequence. Problematic sequence will begin strong but rapidly lose signal strength until there is no sequence data. Therefore, read lengths are typically shorter for these templates. Figure 1 illustrates this rapid decline in signal strength.
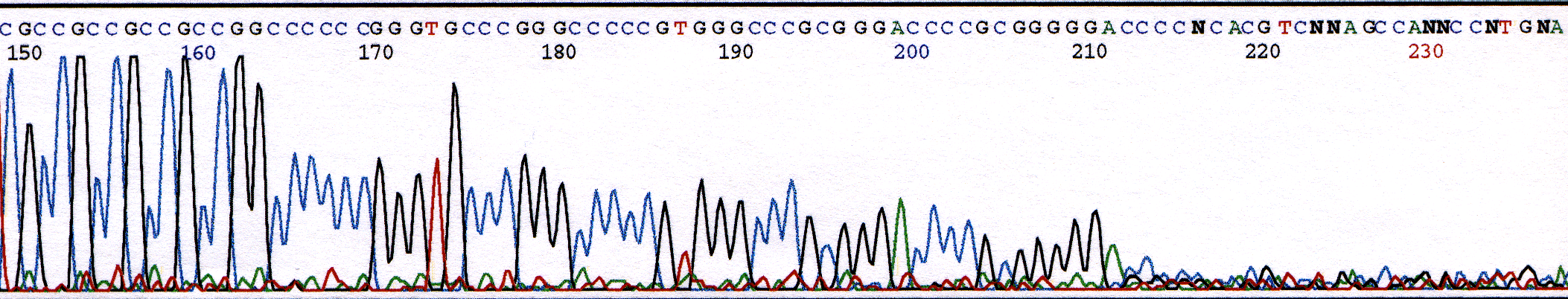
Figure 1. Chromatogram illustrating DNA sequencing data with high GC-content.
A problem with secondary structure is not exclusive to GC-rich template. Secondary structure caused by short regions of high GC-content is not uncommon. These regions can have secondary structure that the enzyme is unable to melt and process through. The secondary structure is observed as an abrupt stop in the sequence (Figure 2).
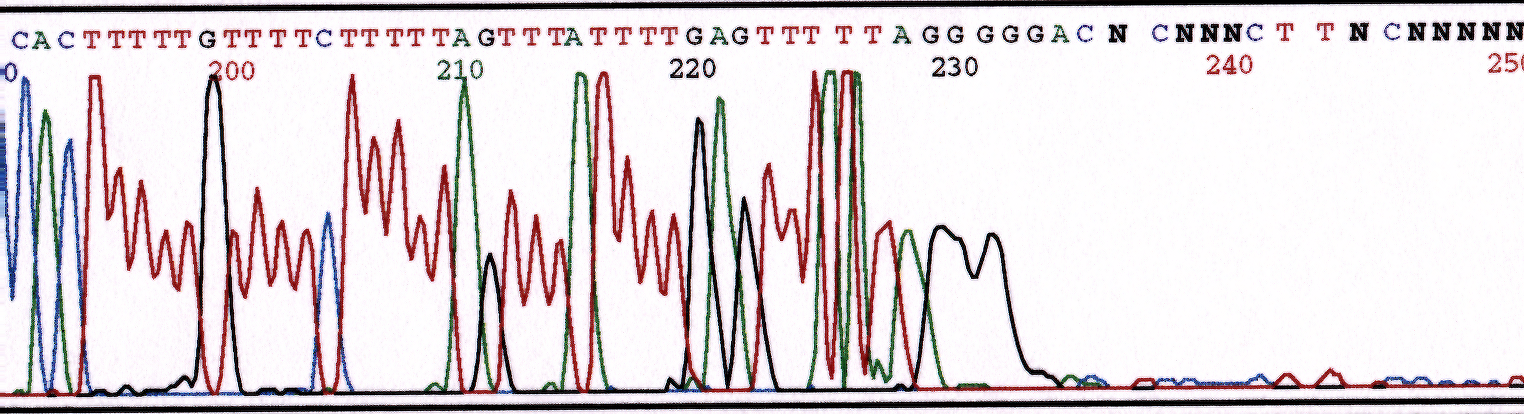
Figure 2. Chromatogram illustrating abrupt stop point due to secondary structure.
Repetitive Region
Repetitive regions are difficult for the enzyme to process through without dissociating from the template. Usually, as observed in the example below, the signal decreases to the point that no further sequence can be obtained.
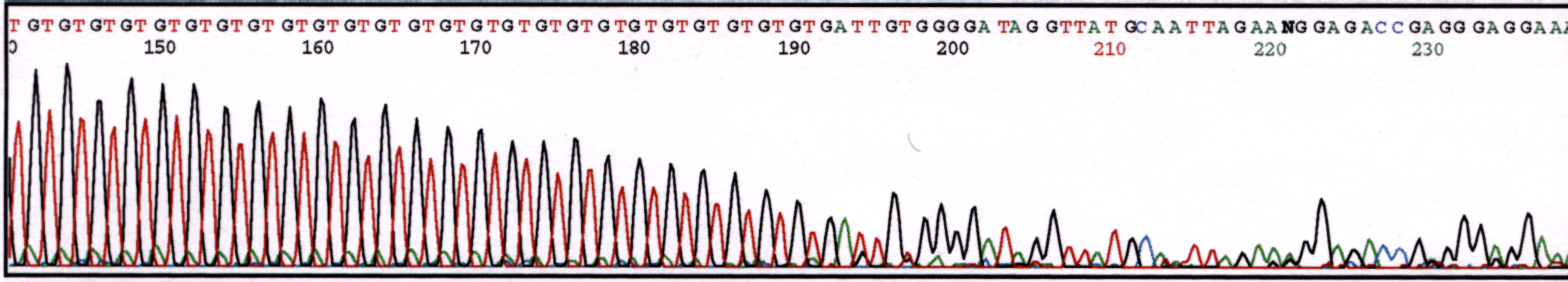
Figure 2. Chromatogram illustrating loss of signal due to repetitive region.
Homoplymeric Region
Poly A tails are difficult for the enzyme to process through. A "stutter" effect is observed in the sequence directly downstream of the poly A region. The disassociation and association of the enzyme with the template cause this effect as it processes through the poly A region. A wave appearance with the four dyes will be observed. Notice the increased number of N's directly following the poly A region in Figure 3.
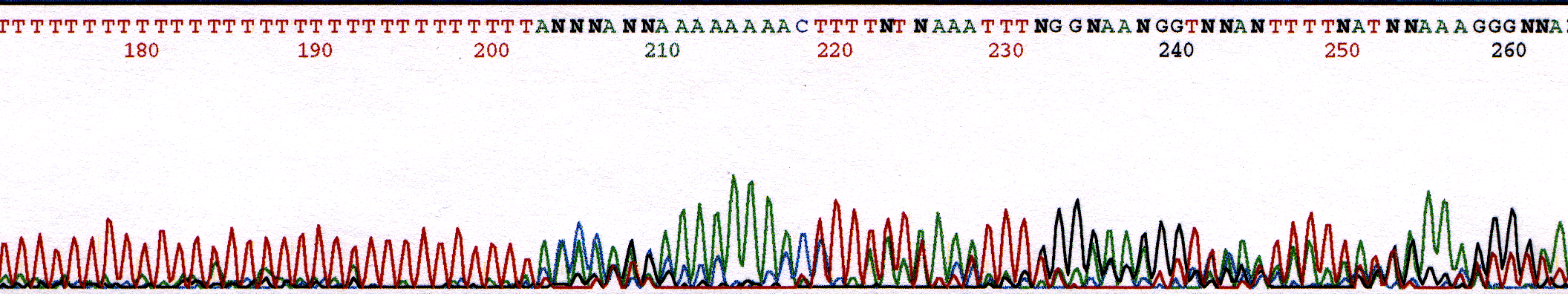
Figure 3. Chromatogram illustrating stutter effect proceeding poly A region.
Other homopolymeric regions such as the run of G's shown in Figure 4 also causes problems for the polymerase. In this example, the enzyme is unable to process through the G's and disassociates from the template.
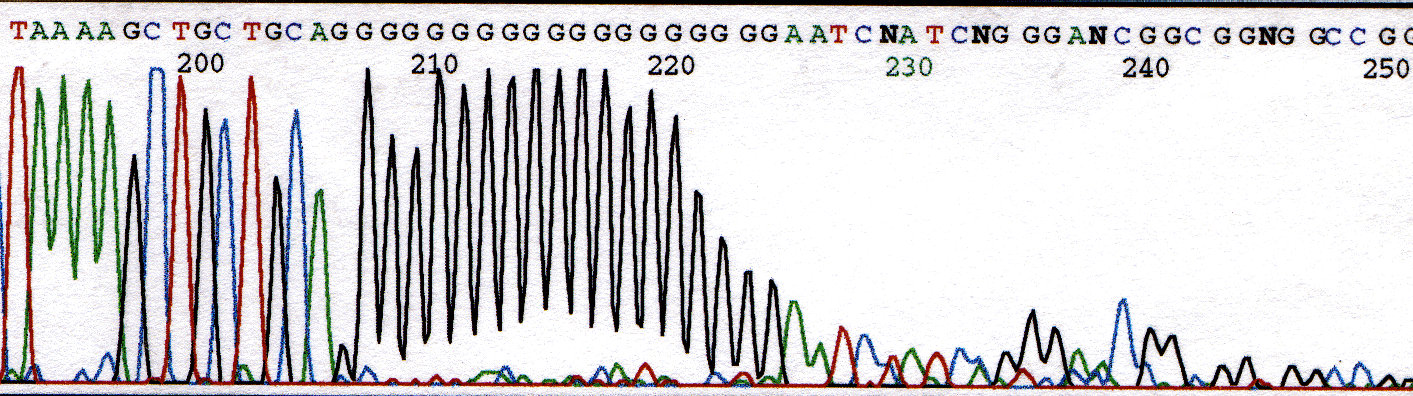
Figure 4. Chromatogram illustrating loss of signal due to homopolymeric region
